
Git学习笔记
源码管理先后用过CVS、SVN和RTC,但自从12年接触Git和Github,就深深的迷上了她。Git是Linus Torvalds为了方便管理Linux代码而开发的分布式源码管理系统,个人认为Git的优点主要是方便大规模协作。Git的客户端有很多,各大IDE也都集成了自己的客户端,但个人还是喜欢使用命令行的方式,原因在于刚开始学Git的时候都是看的命令行的教程,另一方面不太习惯Eclipse的Git插件,最重要的是觉得命令行很酷。本文主要是记录一些基本的Git命令,比较凌乱,不成系统,主要还是给自己看,方便查阅。
配置相关
git --version // 查看git版本
git help config // 查看config命令的帮助文档
git config --list // 列出所有配置项
git config --global user.name "Johnny Wang" // 设置提交代码时显示的作者名字
git config --global user.email archer.wq@gmail.com // 设置提交代码时显示的作者Email
--global参数:修改的是~/.gitconfig--system参数:修改的是/etc/.gitconfig- 不加参数:修改的是当前working dir里的.git/config
基本命令
git init // 初始化git目录
git add README // untracked -> staged | modified -> staged | conflicted -> resolved
git status // 列出当前repository的状态,包括这几种:untracked, modified, staged, unmodified
- Tracked files are those which were in the last snapshot or files which have been newly staged into the index. They can be unmodified, modified, or staged.
- Untracked files are all other files which were not in the last snapshot and have not been added to the index.
- Git工作区:本地数据目录、工作目录、暂存区域

git commit -m "My first commit." // 提交修改,staged -> unmodified
git commit -a -m "My first commit." // 加-a参数 提交之前不需要运行git add, 仅针对tracked的文件
- It is good practice to start the message with a short first line summarizing the change followed by a blank line and then the message body.
忽略特定文件
在repository根目录下建一个.gitignore文件,添加一些文件或目录,git status将不会列出,git commit也不会提交
*.[oa] // 忽略所有.o 或 .a 结尾的文件, 包括子目录里的
!lib.a // 但 lib.a 除外
/TODO // 忽略项目根目录下的 TODO 文件,不包括 subdir/TODO
build/ // 忽略 build/ 目录下的所有文件
doc/*.txt // 忽略 doc/notes.txt 但不包括 doc/server/arch.txt
查看提交日志
git log // 显示所有commit
git log -2 // 显示最近两个commit
git log -p -2 // 显示最近两次commit及改动的文件
git log -stat // 显示所有commit及其统计信息
git log --pretty=oneline --graph // 字符图形单行显示
git log --pretty="%h:%s" --author=Johnny --since="2014-01-01" --before="2014-08-15" --no-merges // 更多限制条件…
gitk // 完全图形化界面显示
比较、删除、重命名
git diff // modifed vs. staged
git diff --cached // staged vs. last commit
git rm test.py // 从staged删除,并且从working dir里删除
git rm -f test.py // 针对modified & staged的情况
git rm --cached test.py // 不删working dir
git mv test.py test_new.py // 重命名,背后实际为mv test.py test_new.py -> git rm test.py -> git add test_new.py
修改、撤销
git commit -m "Initial commit." // 第一次提交
git add forgotten_file // 这个文件忘了提交,加上
git commit // 第二次提交,并且可以修改comment, 这次提交是对第一次提交的修补,最终合并为一个
Do not amend commits if they have already been published to a shared repository since this may disturb others if they already based their changes on the published change.
git reset HEAD test.py // staged -> 原有状态,相当于取消git add
git rest --soft HEAD~1 // undo最近一次提交,适用于还没有push的情况,HEAD~1: HEAD前一个commit, –soft: 只删commit不删working dir
git revert HEAD // undo最近一次提交,适用于已经push的情况,will push a new commit to undo the last commit
git checkout -- test.py // 撤销修改,针对:modified but not staged
标签
git tag v1.0.0 // 给当前HEAD添加轻量级tag
git tag -a v1.0.0 -m "First stable version." // 给当前HEAD添加annotated tag
git tag v0.9.5 9fceb2 // 给之前的一个commit打tag
git tag // 列出所有tag
git tag -l “v0.9.*” // 列出所有v0.9.开头的tag
git show v1.0.0 // 查看tag详细信息
git tag -d V1.0.0 // 删除本地tag
git push origin V1.0.0 // 发布tag
git push origin --tags // 发布所有tag
git push origin :V0.9.5 // 删除远程tag
分支
git branch issue53 // 创建issue53分支,指向HEAD
git checkout issue53 // 切换issu53分支,HEAD->issue53
git checkout -b issue53 // 创建issue53分支并切换到这个分支
git branch // 列出所有分支
git branch -v // 列出所有分支最近一次commit
git branch --merge // 列出与当前分支合并的所有分支
git branch --no-merge // 列出没有与当前分支合并的所有分支
git branch -d issue53 // 删除已经合并的分支
git branch -D issue53 // 强制删除未合并的分支
-
Git仓库的三种对象:commit, tree, blob:

- git add做的事情是:
1) 对文件做checksum;
2) 把文件存到repository;
3) 把checksum放到staging区。 - git commit做的事情是:
1) 对项目目录及子目录做checksum,生成tree对象(包含文件名到blob的对应关系)存到repository;
2) 创建commit对象:包含指向tree & parent commit的指针及其他信息。 -
后一个commit保存对前一个commit的指针:

- branch实际上是一个指向某个commit的指针:

- HEAD指针指向当前工作分支
合并
git checkout master // 切到master分支
git merge issue53 // 合并issue53分支到当前分支
- 合并之前:

- 合并之后:
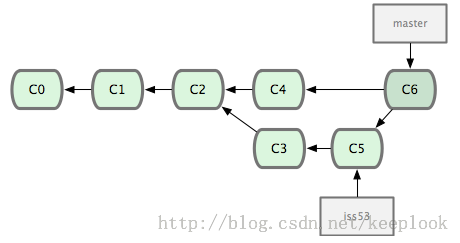
- merge有两种情况:
1) 创建issue53分支后当前分支没有新的commit, 那么合并issue53分支到当前分支只需要修改HEAD指针即可,这种情况称为fast-forward;
2) 创建issue53分支之后当前分支有新的commit, 合并issue53到当前分支时会创建一个新的commit包含两个分支自交叉点以后的修改,合并后HEAD指向这个新的commit. 即上图情况。 - 如果两个分支对同一文件进行了修改,那么merge会报冲突,文件会包含两个分支的修改:In the file content, the area where a pair of conflicting changes happened is marked with markers «««<, =======, and »»»>. The part before the ======= is typically your side, and the part afterwards is typically their side. 需要手工修改这个文件,修改完毕之再git add & git commit.
衍合
git checkout -b experiment
commits on experiment goes here…
meanwhile other team members made some commits on master…
rebase之前:

git rebase master // 把当前分支修改衍合到master分支:把自分叉点开始experiment的修改在master分支重做一遍产生一个新的commit, 这个新的commit其实跟git merge产生的一模一样,结果是master分支新增了一个commit, 当前分支还是experiment(HEAD指向新的commit)
rebase之后:

git checkout master
git merge experiment // 这儿是一次fast forward merge
衍合能产生一个更为整洁的提交历史,但永远不要衍合那些已经推送到公共仓库的更新,我们只能把衍合当成一种在推送之前清理提交历史的手段。
远程操作
git clone https://github.com/archerwq/python-toobox.git // 自动创建一个名为python-toobox的本地库,添加一个名为origin的远程库,并下载其中所有的数据,建立一个指向它的 master 分支的指针,在本地命名为 origin/master,但你无法在本地更改其数据,接着建立一个本地的master分支,指向origin上master分支相同的位置
git clone https://github.com/archerwq/python-toobox.git python-tutorial // 功能同上,只不过创建的本地库名字跟远程库不同
git remote add origin https://github.com/archerwq/java-toolbox.git // 给当前库添加一个远程库,命名为origin
git remote rename origin pb // 重命名远程库
git remote rm pb // 删除远程库
git remote // 列出当前库添加的所有远程库名
git remote -v // 列出地址信息,-v是verbose缩写
git remote show origin // 列出某个远程库的详细信息
远程分支(remote branch):(远程仓库名)/(分支名),如origin/master,是对远程仓库状态的索引,它们是一些无法移动的本地分支,只有在进行 Git 的网络活动时才会更新,远程分支就像是书签,提醒着你上次连接远程仓库时上面各分支的位置。
git push origin issue53 // 把本地分支issue53推送到远程origin库
git checkout -b issue53 origin/issue53 // 创建本地分支issue53来跟踪远程分支refs/remotes/origin/issue53
git push origin :issue53 // 删除远程分支issue53
git fetch origin // 获取远程库的branch/commit等信息更新本地数据库,相当于同步一下
When you git fetch, git retrieves any commits from the target remote that you do not have and stores them in your local repository. However, it does not merge them with your current branch. This is particularly useful if you need to keep your repository up to date but are working on something that might break if you update your files. To integrate the commits into your local branch, you use git merge. This combines the specified branches and prompts you if there are any conflicts.
git pull origin // 获取远程库数据并自动做merge操作
When you use git pull, git tries to automatically do your work for you. It is context sensitive, so git will merge any pulled commits into the branch you are currently working in. One thing to keep in mind is that git pull automatically merges the commits without letting you review them first. If you don’t closely manage your branches you may run into frequent conflicts.
Comments